 Affiliate marketing looks simple on the surface: you share a link, someone clicks it, makes a purchase, and you get paid. Easy, right?
Affiliate marketing looks simple on the surface: you share a link, someone clicks it, makes a purchase, and you get paid. Easy, right?
Behind the scenes, though, there’s a surprisingly sophisticated tracking system making sure the right affiliate gets credit for the right sale. Without accurate tracking, affiliate marketing wouldn’t work at all.
So let’s break it down in plain English—no jargon overload, no mystery boxes. By the end of this, you’ll understand exactly how affiliate marketers track commissions, why tracking sometimes fails, and how platforms keep everything fair (most of the time).
The Big Picture: What Is Affiliate Tracking?
At its core, affiliate tracking answers three simple questions:
- Who sent the visitor?
- What did the visitor do?
- Does that action qualify for a commission?
To answer those questions, affiliate platforms rely on a mix of:
- Unique tracking links
- Cookies and identifiers
- Attribution rules
- Backend reporting systems
All of this happens automatically, usually in milliseconds.
Step 1: The Affiliate Link (Everything Starts Here)
Every affiliate is given a unique tracking link by an affiliate program or network.
That link contains:
- The merchant’s website URL
- The affiliate’s unique ID
- Sometimes a campaign or ad ID
A simplified example might look like this:
https://merchant.com/product?aff_id=12345
When someone clicks that link, the system instantly knows:
“This visitor came from affiliate #12345.”
Affiliate networks like Amazon Associates, ClickBank, and CJ Affiliate generate these links automatically so affiliates don’t have to worry about the technical side.
Step 2: Cookies (The Digital Breadcrumbs)
Once a visitor clicks your affiliate link, a cookie is placed in their browser.
A cookie is a small piece of data that says something like:
“This person was referred by affiliate #12345 at 3:42 PM on Tuesday.”
Why Cookies Matter
Cookies allow commissions to be credited even if the visitor doesn’t buy right away.
For example:
- Someone clicks your link today
- Leaves the site
- Comes back tomorrow and buys
If the cookie is still active, you get the commission.
Cookie Duration (A Big Deal)
Each affiliate program sets its own cookie lifespan:
- 24 hours (common with Amazon)
- 7 days
- 30 days
- 90 days or more
Longer cookie durations = higher chance you get paid.
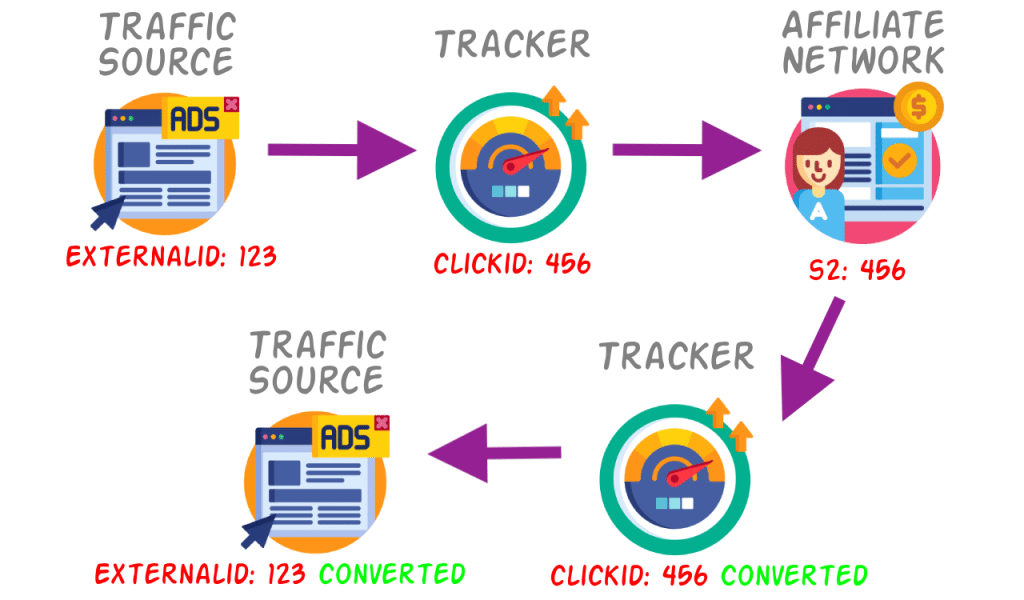
Step 3: Tracking Pixels and Server Calls
Cookies alone aren’t enough. To confirm a sale, affiliate systems use tracking pixels or server-to-server (S2S) tracking.
Here’s what happens when a purchase is completed:
- The buyer reaches the “Thank You” or confirmation page
- A tracking pixel fires or a server call is made
- The affiliate platform is notified:
-
- Sale amount
- Product ID
- Affiliate ID
- Order status
This is how the system knows:
“Yes, this sale actually happened—and here’s who gets paid.”

Step 4: Attribution Models (Who Gets Credit?)
Here’s where things get interesting.
What if:
- A user clicks multiple affiliate links?
- They see ads, read blogs, and watch videos before buying?
Affiliate programs solve this with attribution rules.
Common Attribution Models
Last-click attribution
- The last affiliate link clicked before purchase gets the commission
- Most common model
First-click attribution
- The first affiliate who referred the visitor gets credit
Multi-touch attribution
- Commissions are split between multiple affiliates
- Less common, more complex
Most beginner-friendly programs stick with last-click because it’s simple and easy to enforce.
Step 5: Affiliate Dashboards and Reporting
Once a sale is tracked, it appears in the affiliate’s dashboard.
Dashboards typically show:
- Clicks
- Conversions
- Conversion rate
- Commission earned
- Pending vs approved commissions
This data helps affiliates:
- See what content is working
- Optimize traffic sources
- Spot tracking issues early
Behind the scenes, these dashboards pull data from logs, cookies, pixels, and databases—all tied back to that original affiliate link.
Step 6: Validation, Holds, and Fraud Checks
Not every tracked sale gets paid instantly.
Most programs apply a holding period, often 14–60 days.
Why?
- Refunds
- Chargebacks
- Fraud prevention
During this time, commissions show as:
- Pending
- Processing
Once the hold period ends and the sale is confirmed as valid, the commission becomes approved.
This protects merchants from paying out on sales that don’t stick.
Server-to-Server Tracking (The Modern Upgrade)
Traditional cookie tracking has weaknesses:
- Ad blockers
- Browser privacy restrictions
- Cookie deletion
To fix this, many platforms now use server-to-server (S2S) tracking.
Instead of relying on the user’s browser:
- Data is passed directly between servers
- Tracking becomes more accurate
- Privacy compliance improves
S2S tracking is especially common in:
- SaaS affiliate programs
- High-ticket offers
- Subscription-based products
Cross-Device Tracking (Yes, It’s a Thing)
What if someone:
- Clicks your link on their phone
- Buys later on their laptop?
Basic cookie tracking struggles here.
Advanced systems solve this using:
- Logged-in user accounts
- Email-based identifiers
- Platform-level attribution
This is more common with large ecosystems and membership-based platforms than simple retail offers.
Why Tracking Sometimes Fails
Even with all this tech, commissions don’t always track correctly.
Common reasons:
- Cookies blocked or deleted
- Ad blockers preventing pixels
- Browser privacy features
- User switching devices
- Incorrect affiliate link formatting
This is why experienced affiliates:
- Test links regularly
- Screenshot dashboards
- Use tracking IDs or sub-IDs
Sub-IDs and Custom Tracking (Power User Stuff)
Many affiliate links allow sub-IDs, which affiliates use to track performance at a granular level.
Example:
?aff_id=12345&subid=blogpost1
This lets affiliates see:
- Which blog post converted
- Which email link worked best
- Which ad produced the sale
It’s not required—but it’s incredibly useful once you scale.
Payments: The Final Step
Once commissions are approved, affiliates get paid via:
- PayPal
- Direct deposit
- Wire transfer
- Platform credits
Payment schedules vary:
- Weekly
- Bi-weekly
- Monthly
Minimum payout thresholds often apply (e.g., $50 or $100).
Why Accurate Tracking Is Everything
Affiliate marketing runs on trust:
- Affiliates trust platforms to track honestly
- Merchants trust affiliates to send real buyers
If tracking fails, the whole system breaks down.
That’s why modern affiliate platforms invest heavily in:
- Redundant tracking systems
- Transparent reporting
- Anti-fraud technology
Final Thoughts
Affiliate commission tracking isn’t magic—it’s a well-orchestrated system built on links, cookies, attribution rules, and backend reporting.
As an affiliate:
- You don’t need to master the tech
- But understanding how it works helps you troubleshoot issues, choose better programs, and scale smarter
And as a merchant:
- Reliable tracking is non-negotiable
- It’s the foundation of any successful affiliate program